The 4C's
Cut
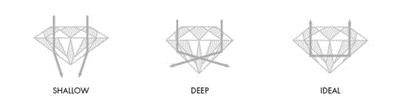
We love diamonds because they sparkle. How well a diamond is cut, will determine how much sparkle it will have. The shape of the diamond, it’s proportions, symmetry and polish produce different optical effects. Looking at the images below, you can see how light in an ideal cut diamond will create even reflections and produce maximum brilliance. A diamond cut too deep will have dark areas, unbalanced reflections and lack of brilliance. A diamond cut too shallow will look milky, have unbalanced reflections and will have a lack of brilliance.
Clarity
Diamond crystals formed in the earth that are crystal clear are so rare that only 2% of the worlds diamond supply is crystal clear or flawless. Diamond crystals were formed from a cooling liquid state and anything foreign within this liquid was eternally embedded inside. When diamonds cooled into their crystal form, most experienced cooling fractures as well, which look like white feathers or cracks. We prefer to use the term natural characteristics rather than flaws, inclusions or imperfections because they create a diamonds beautiful personality. Clarity is graded by viewing a diamond through the top using 10x magnification. There are 6 main categories of clarity and each have guidelines based on how many natural characteristics there are, their size, location, direction, colour and how easily they are seen. The clearer a diamond is, the higher it is graded. The higher the grade, the rarer and more valuable it is.
FL – Flawless –Perfection on the inside and the outside.
IF – Internally Flawless – Perfection on the inside with a minute little something on the outside.
VVS – Very Very Slightly Included – Minute natural characteristics very difficult to see under 10x magnification.
VS – Very Slightly Included – Natural characteristics difficult to see under 10x magnification.
SI – Slightly Included – Natural characteristics easily seen under 10x magnification but not visible to your naked eye.
Il – Included –Natural characteristics sometimes seen with the naked eye and obvious under 10x magnification.
I2 and I3 – Included – Obvious natural characteristics visible to your naked eye.
Colour
Colour is the natural range of tint in a diamond. Diamonds formed from a liquid state of carbon deep in the earth under intense heat and pressure. If a trace of another element solidified when a diamond crystal was forming it altered its colour. Nitrogen is the most common element which adds a tint of yellow to diamonds. The amount of nitrogen within a crystal dictates how yellow it will become.
Diamonds form in every colour of the rainbow as well as black and white. All diamonds other than white are categorized as fancy and graded for colour on a different scale.
Colourless: D-E-F
Near Colourless: G-H-I-J
Faint Yellow: K-L-M
Very Light Yellow: N to R
Light Yellow: S to Z

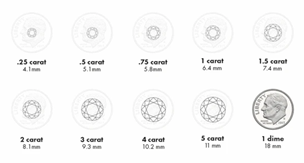
Carat Weight
Carat weight is the physical weight of a diamond on a scale. Diamonds have their own unique system of weight that has existed for thousands of years. The word “carat” originated from the carob tree which produced seeds that were always the same size and weight making them a reliable and available resource of weight for reference.
One carat weighs 0.20 grams on a scale. All weights are referenced to one carat, or in other words, anything weighing less than one carat is referred to as under a carat, where anything weighing over a carat is more than a carat.
Because diamonds are so valuable, this weight system had to be broken down further to be more precise. A fraction of a carat could mean a price difference of thousands of dollars so accuracy is critical when valuing a diamond for sellers and buyers. Therefore, one carat is broken down into 100 points, the same concept as 100 pennies in one dollar. One carat = 100 points.
Carat weight is written using decimal numbers, the same as units of money. A one dollar bill is written $1.00. A one carat diamond is written 1.00ct. and the word “carat” is abbreviated to “ct”. A diamonds weight can be expressed in points or carats.
Shape
A diamonds shape is not the same as a diamonds cut. Shape is the external form a diamond is cut into. 75% of the worlds diamond supply is cut into the round shape because its symmetry, when cut properly, has the most brilliance compared to other shapes of equal quality. Each diamond shape has different attributes that affect the price and quality grade.